Blue Light
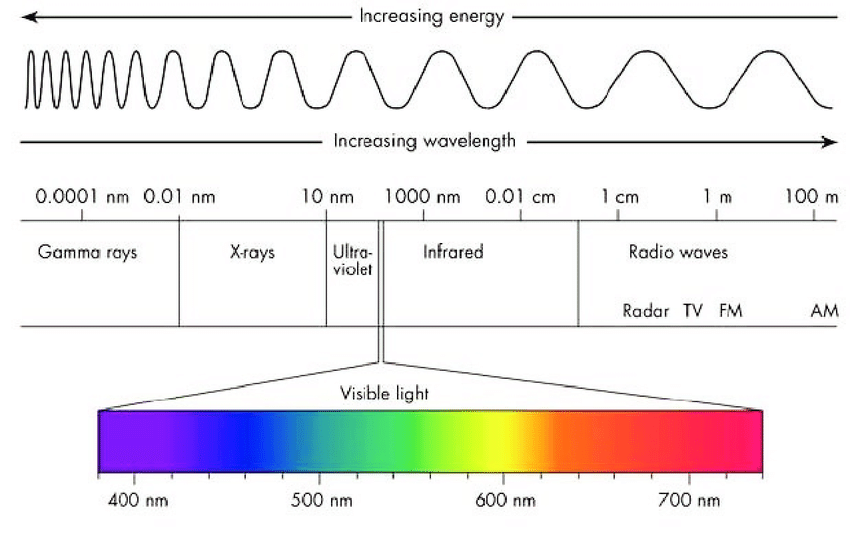
Blue Light is a spectrum of light ranging from 380 nm – 500 nm
The Visible light spectrum for humans is 380nm - 700nm
The suns blue light is unpolarized and most prominent around midday.
Artificial Blue light is polarized and is the only spectrum of light that is present in modern LED lighting, all phones, laptops, tablets, TV's and other screens.
Modern LED lighting also have high flicker rates, which means the light flickers faster then the human eye can see.
What Is Blue Light?
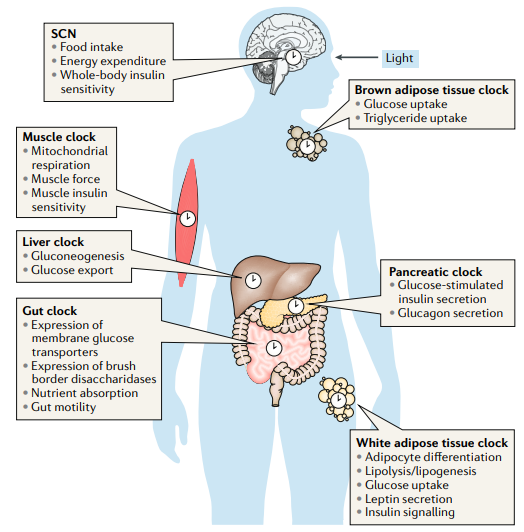
Blue light enters the human body through the eyes and skin as we have melanopsin everywhere in the human body. Melanopsin is a blue light detector.
Blue light enters your eye through the retina then to the supercoasmatic nucleus, which is an atomic clock that controls all the clocks in your body. This is how our body's master clock know what time of day it is.
Blue light enters your skin through melanopsin, this our the clocks in our skin get the input signal for what time of day it is.
How blue light intacts with the body
Effects of Blue Light on the Human Body
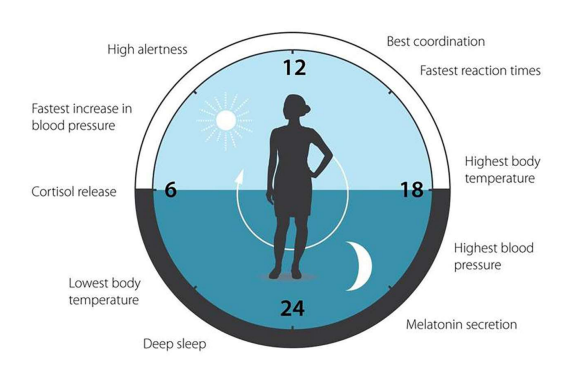
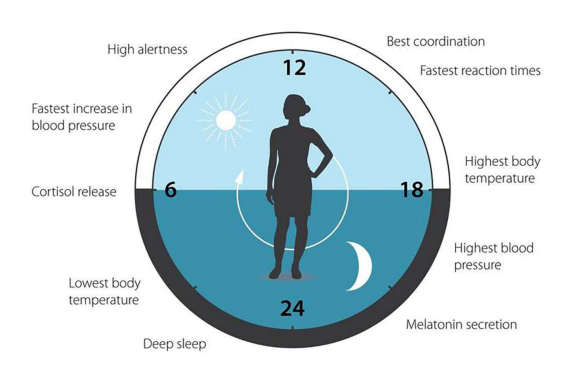
Blue light enters your eye through the retina then to the supercoasmatic nucleus. Therefore exposing your retina to this light signals to your brain constantly that is midday.
Midday is the time of day that we are evolutionarily meant to be most awake and aware. This is the time of day that our autonomic nervous system is also most engaged.
Thus if you expose yourself to blue light, especially in the evenings it will disrupt your body’s ability to sleep because you will be more awake and your clocks will be tricked to think it’s midday.
Disrupts the body's Circadian Rhythm
Melatonin is a hormone of dark that builds up in your body as you expose your skin and eyes to natural sun throughout the day.
As the sun lowers the light passes through the supercoasmatic nucleus, signalling to the pineal gland to release melatonin into your bloodstream, thus making you sleepy and eventually leads to a good night sleep.
However exposing your eyes and skin to blue light surpresses the buildup of melatonin, therefore it will hinder your ability to fall asleep. Also it has the potential to limit your body’s ability to perform autophogy (cell repair) as melatonin controls this mitochondrial DNA mechanism.
Supresses Melatonin
Increases blood glucose & insulin
Blue light destroys DHA in the cell membrane of mitochondria which leads to electron steal syndrome. This brings about short circuiting of your mitochondria and you can't turn light signals into electric signals
Increases your appetite by making you leptin resistant
Liberates vitamin A in aldehyde form leading to a dielectric collapse (Can't Decipher electromagnetic information)
Flicker from LEDs stresses the muscles of the eyes, overstimulates the sympathetic nervous system thus putting you in the flight of fright mechanism. Can also cause migraines & cognitive disfunction.
Other Effects
How we can block blue light
#2: Wear Blue light blocking glasses
By wearing blue light blocking glasses you can protect your eyes when looking at screens during the day time and night time. During the day you should wear the yellow lenses and during the night time you should wear the red lenses.
Blue light blocking glasses can be purchased from the following websites:
EMR-Tek: follow this link https://www.emr-tek.com/SACREDELECTRICAL and enter code: SACREDELECTRICAL at checkout to receive discount at checkout.
Baxter Blue: follow this link https://www.baxterblue.com.au/?ref=sacredelectrical and enter code: SACRED_ELECTRICAL for 15% discount at checkout.
Chroma: follow this link https://getchroma.co/sacredelectrical and enter code SACRED_ELECTRICAL for 15% discount at checkout.
#1: Replacing LED lights with healthier lights
Installing full spectrum lights
Installing blue light blocking lights
Having candles at night time
#3: Replace laptop with Daylight Computer
Daylight computer has released a new tablet that has removed the blue light from the hardware and now uses red light In the screen. They also have a red light tablet for kids now too.
Daylight Computer @ https://buy.daylightcomputer.com/SACREDELECTRICAL & enter code SACREDELECTRICAL at checkout for $25 USD discount.
#4: Shield screens from blue-light
Blue light from screen can be reduced by putting a blue light blocking glass or plastic over it or by installing a red light filter on your screens.
Blue light filter apps that you can use:
Iris: https://iristech.co/
Twilight
F-flux
Blue light blocking glass & Plastics can be purchased from the following sites:
Acme plastics. https://www.acmeplastics.com/
Block Blue Light: https://www.blockbluelight.com.au/products/blue-blocking-screen-filter-iphone
Ocu Shield: https://www.ocushield.com/
Research:
Sources about blue light & its interaction with the human body
Melatonin and insulin are solar metronomes
Dr. Jack Kruse June 25th 2016
https://jackkruse.com/time-17-melatonin-insulin-solar-metronomes/
Hypoxia #4: Red Light, Blue Light, 1.2.3
Dr Jack Kruse February 20th 2020
Quantum Biology #12: Do We need DNA to tell time
Dr. Jack Kruse 21st July 2013
https://jackkruse.com/quantum-biology-12-do-we-need-dna-to-tell-time/
Studies about artificial lights effects on Circadian rhythms & Melatonin
Effects of light on human circadian rhythms sleep and mood
Blume, C., Garbazza, C., & Spitschan, M. (2019). Effects of light on human circadian rhythms, sleep and mood. Somnologie, 23(3), 147–156.
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11818-019-00215-x
Impact of daytime light exposure on sleep and mood in office workers
Figueiro, M. G., Steverson, B., Heerwagen, J., Kampschroer, K., Hunter, C. M., Gonzales, K., Plitnick, B., & Rea, M. S. (2017). The impact of daytime light exposure on sleep and mood in office workers. Sleep Health, 3(3), 204–215.
https://www.sleephealthjournal.org/article/S2352-7218(17)30041-4/abstract
Impact of windows and daylight exposure on overall health and sleep quality of office wworkers.
Boubekri, M., Cheung, I. N., Reid, K. J., Wang, C. H., & Zee, P. C. (2020). Impact of windows and daylight exposure on overall health and sleep quality of office workers: A case-control pilot study. Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine, 16(2), 203–209.
Melatonin and insulin are solar metronomes
Dr. Jack Kruse June 25th 2016
https://jackkruse.com/time-17-melatonin-insulin-solar-metronomes/
J. K. Phillips, A, Vidafar, P & Burns, A 2019, ‘High sensitivity and interindividual variability in the response of the human circadian system to evening light', Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences,Vol. 116 | No. 24 June 11, 2019
Association between light at night, melatonin secretion, sleep deprivation, and the internal clock: Health impacts and mechanisms of circadian disruption
Yvan Touitou, Alain Reinberg, David Touitou
March 2017
Life Sciences 173(Suppl. 3):94-206
Effects of Light on Cognitive Brain Responses Depend on Circadian Phase and Sleep Homeostasis
Vandewalle, Gilles, her, Simon N.Wuillaume, Catherine Balteau, Evelyne
Degueldre, Christian Luxen, André Dirk, Derk-Jan Maquet, Pierre
Journal of biological rhythms, vol 26 no 23, June 2011, pg. 249 - 259
https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/0748730411401736
Evening light exposure to computer screens disrupts human sleep, biological rhythms, and attention abilities
A. Green, M. Cohen-Zion, A. Haim & Y. Dagan
Pages 855-865 | Received 15 Mar 2017, Accepted 26 Apr 2017, Published online: 26 May 2017
Recommendations for daytime, evening, and nighttime indoor light exposure to best support physiology, sleep, and wakefulness in healthy adults
Timothy M. Brown,George C. Brainard, Christian Cajochen, Charles A. Czeisler, John P. Hanifin, Steven W. Lockley, Kenneth P. Wright Jr
https://journals.plos.org/plosbiology/article?id=10.1371/journal.pbio.3001571
Studies on effect of LED lights flicker
Potential Biological and Ecological Effects of Flickering Artificial Light
Richard Inger, Jonathan Bennie, Thomas W Davies, Kevin J Gaston
May 2014
Influence of Light Emitting Diode-Derived Blue Light Overexposure on Mouse Ocular Surface
Hyo Seok Lee, Lian Cui, Ying Li, Ji Suk Choi, Joo-Hee Choi, Zhengri Li, Ga Eon Kim, Won Choi, Kyung Chul Yoon,
Studies relating to increased insulin & Blood glucose
Effects of Cell Phone Radiofrequency Signal Exposure on Brain Glucose Metabolism
Nora D Volkow, Dardo Tomasi, Gene-Jack Wang, Paul Vaska, Joanna S Fowler, Frank Telang, Dave Alexoff, Jean Logan, Christopher Wong.
JAMA. 2011 Feb 23;305(8):808-13. doi: 10.1001/jama.2011.186. PMID: 21343580; PMCID: PMC3184892.
Artificial Light at Night and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Jong-Ha Baek, Yong Zhu, Chandra L. Jackson, Yong-Moon Mark Pararkfg
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal 2024;48(5):847-863. DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2024.0237
Published online: September 1, 2024
Morning and Evening Blue-Enriched Light Exposure Alters Metabolic Function in Normal Weight Adults
Ivy N. Cheung, Phyllis C. Zee, Dov Shalman, Roneil G. Malkani, Joseph Kang, Kathryn J. Reid
Published: May 18, 2016
https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.015560
I'm not your average electrician. I've been researching how light effects the human body for years now and have been assuring it aligns to science. All the studies can be seen below.